After the Manitoba, Canada, public health agency reported data showing those fully vaccinated (not boosted) for COVID-19 are at higher risk of dying from the virus compared to unvaccinated individuals, health officials stopped reporting on the data — a trend seen in other countries, including Scotland, the U.K. and the U.S.
Manitoba, population 1.4 million, was the first Canadian province whose public health agency reported data showing those who are fully vaccinated (not boosted) for COVID-19 are at higher risk of dying from COVID-19 compared to unvaccinated individuals.
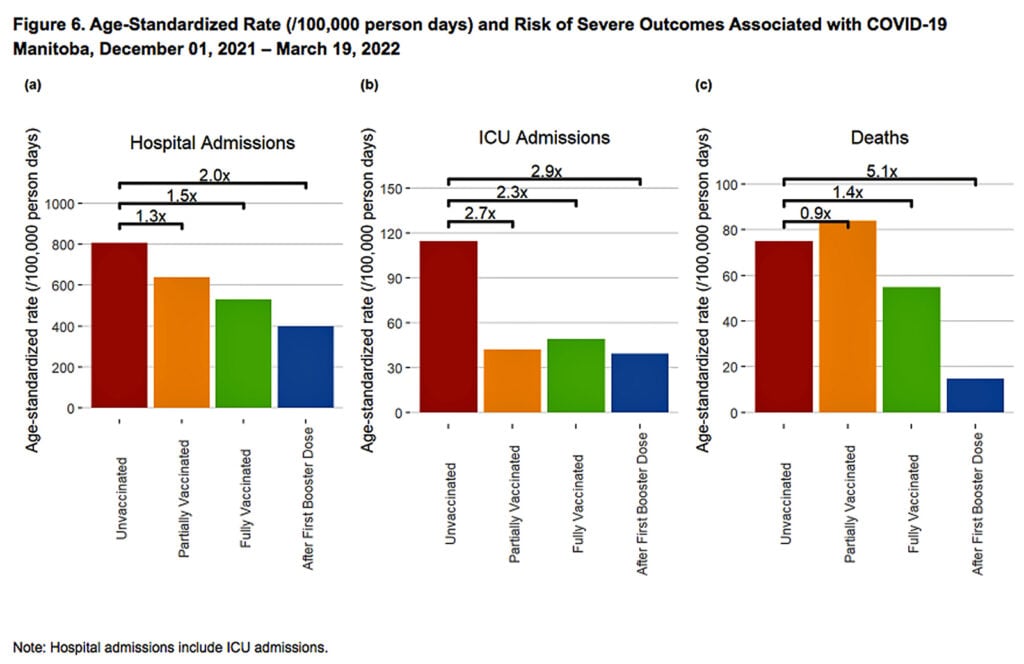
The age-standardized data are from May 2022, but last appeared in Manitoba’s August 3 report:
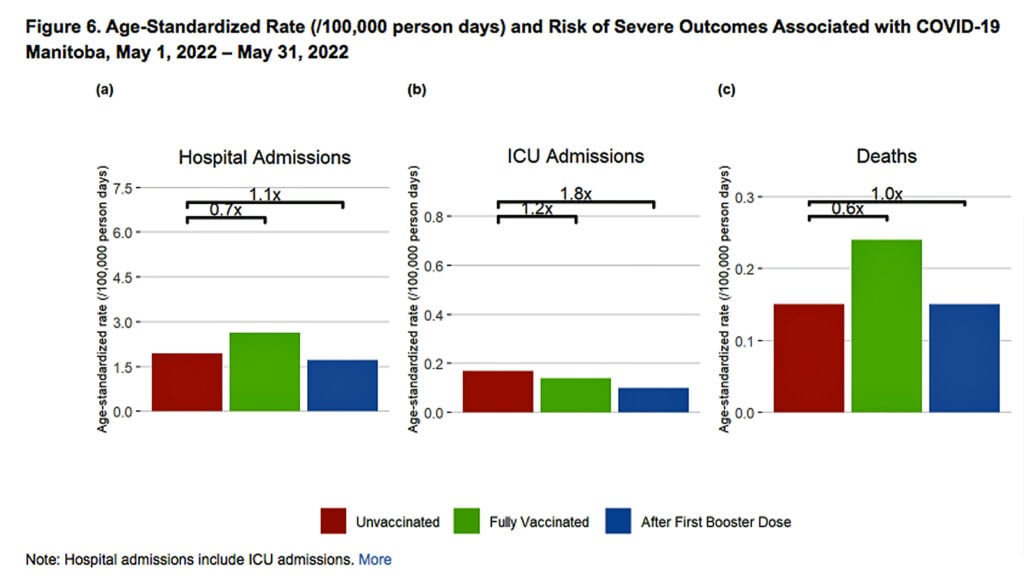
As the figure above indicates, for the month of May, Manitoba Public Health reported a 40% increased risk of death associated with COVID-19 in “fully vaccinated” individuals compared to unvaccinated.
The risk of death for those who were boosted was the same as for unvaccinated individuals.
Though three months old, the May data are, as of this writing, the last reported by the Canadian province.
Manitoba’s trending risk of severe outcomes by vaccination status
The May data on severe outcomes by vaccination status are part of a monthly trend suggesting reduced vaccine effectiveness over time.
By the end of December 2021, 74.7% of Manitobans were vaccinated for COVID-19 and 18.7% were not vaccinated, according to Manitoba Public Health’s weekly report for December 19-25, 2021.
At that time, Manitoba was not reporting on severe COVID-19 outcomes by vaccination status.
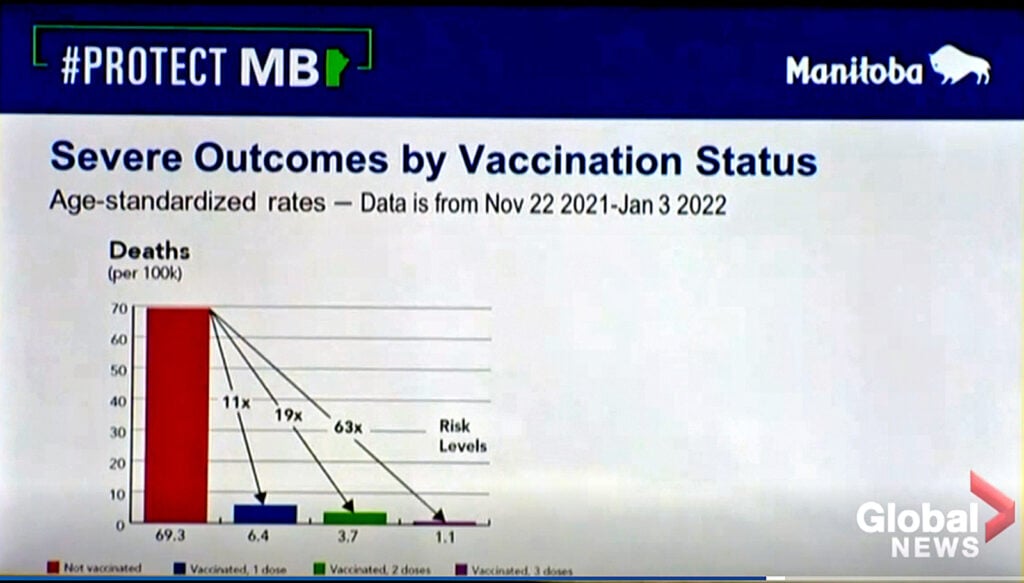
On Jan. 12, 2022, Global News reported that between Nov. 22, 2021, and Jan. 2, 2022, boosted individuals (purple bar) were 63 times less likely to die from COVID-19 than unvaccinated individuals (red bar):
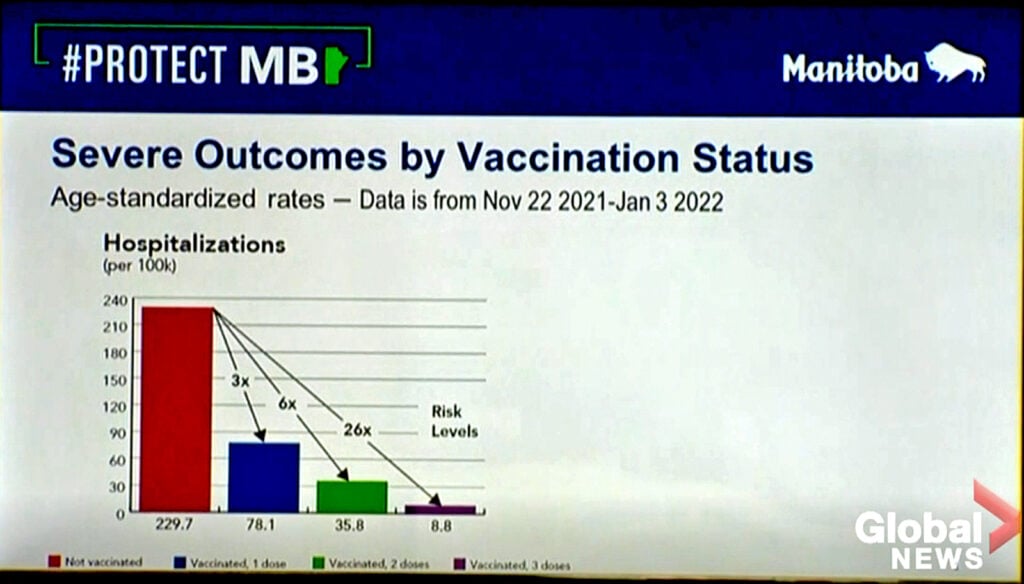
Boosted individuals also were 26 times less likely to be hospitalized:
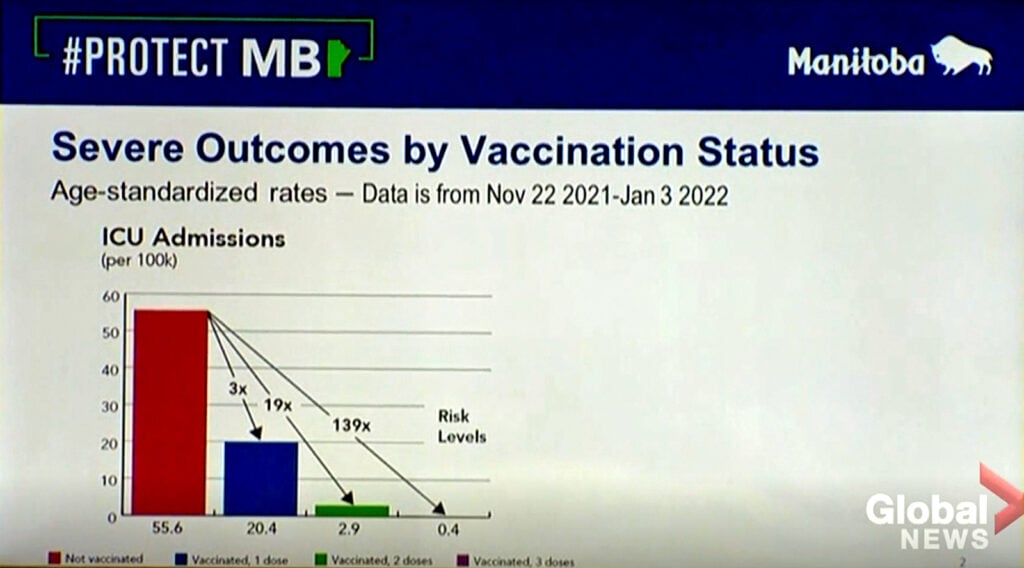
And boosted individuals were 139 times less likely to be admitted to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) than unvaccinated individuals:
The Manitoba Public Health’s weekly reports did not report this data at the time.
Manitoba first reported severe outcomes by vaccination status in March 2022, and then updated the numbers each month for the next three months.
In those reports, the risk of a severe outcome was age-standardized and reported per 100,000 person days.
Age-standardization, also called age-adjustment, is a statistical procedure that allows for the comparison of groups with different age structures. It is used because the risks of death and severe outcomes are different depending on a person’s age.
With COVID-19, for example, it is well known that older adults are at a higher risk of hospitalization and death from COVID-19. If older adults are more likely to opt for vaccination and boosting, then the vaccinated and boosted groups would have a greater proportion of older people, who are at higher risk of severe outcomes, than the unvaccinated group.
Without age-standardization, the statistics would not show the impact of vaccination independent of age.
Here were Manitoba Public Health’s first comparative data around COVID-19 age-standardized severe outcomes:
Though there were nearly 5 of 16 weeks that overlapped with the time window on which Global News reported, the vaccine’s effectiveness against severe outcomes had somehow plummeted.
Then in the subsequent report that covered the month of March only, vaccine effectiveness dropped more (notice the 3 times greater risk of ICU admission in the partially vaccinated):

And in the next report, vaccine effectiveness dropped further still:

Manitoba Public Health, without explanation, stopped reporting the rate of severe outcomes in the “partially vaccinated.”
Finally, the most recent report showed us results from May 2022:

For the month of May, Figure 6 (above) shows that unvaccinated individuals were 40% less at risk of COVID-19-associated death than fully vaccinated individuals, and their risk was the same as boosted individuals.
Unvaccinated people also were 30% less likely to require hospitalization than vaccinated people, and 10% more likely to be hospitalized than boosted people.
Unvaccinated people were more likely to require ICU admission — 20% more than fully vaccinated people and 80% more likely than boosted individuals.
Manitoba did not report on these outcomes for the month of June or any time period since.
Manitoba’s latest report, dated August 11, announced:
“Monthly updates about severe outcomes after vaccination have been discontinued starting Week 31 [July 31-Aug. 6]. Manitoba Health will continue to monitor COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness and report periodically when data allow.”
At the time of this writing, Manitoba Public Heath had not responded to a request to explain why it stopped reporting this data.
Despite their latest data showing an increased risk of death and hospitalizations in vaccinated individuals and no survival benefit in the boosted, the authors paradoxically summarize:
“COVID-19 vaccines continue to provide important protection against serious illness following infection due to all variants of concern (VOC) of COVID-19.”
Public health agencies stop reporting inconvenient data
Though independent journalist Alex Berenson brought attention to this official data, there have been no news reports in the mainstream media about this disquieting trend in Manitoba.
Nor have the media reported on why Manitoba suddenly stopped releasing this data. This appears to be part of a larger trend of public agencies ending reporting on severe COVID-19 outcomes by vaccination status.
For example, the Canadian province of British Columbia (BC), like Manitoba, for a time produced weekly reports that included age-stratified data on severe COVID-19 outcomes by vaccination status.
But at the end of July, the BC Centre for Disease Control website stated, “As of July 28, the Outcomes by Vax and Vax Donut Charts have been retired.”
CTV News Vancouver, a Canadian news station, asked the BC Ministry of Health for an explanation. An emailed response from a ministry spokesperson read, in part:
“As most of the population has now been vaccinated with at least two doses of vaccine and many more have been infected with COVID-19, the data became hard to interpret.”
Ontario, next door to Manitoba, also used to report weekly on severe COVID-19 outcomes by vaccination status.
However, the “COVID-19 Vaccine Data in Ontario” website now states that hospitalization by vaccination status data and cases by vaccination status data will no longer be published as of June 30, and that case rates by vaccination status and age group data will no longer be published as of July 13.
Ontario continues to report deaths by vaccination status, but as raw data in a CSV file that can be downloaded and that requires the person who downloads it to generate the graph.
Scotland stops reporting data due to ‘increasing risk of misinterpretation from growing complexities’
Scotland releases weekly reports and used to report severe COVID-19 outcomes by vaccination status.
In the weekly report released on March 2, Public Health Scotland (PHS) announced that severe outcomes by vaccination status “will no longer be reported on a weekly basis from 16 February 2022.”
Officials said:
“Due to the increasing risk of misinterpretation from growing complexities as the COVID-19 pandemic enters its second year (as described below), PHS has taken the decision to no longer report COVID-19 cases, hospitalisations and deaths by vaccination status on a weekly basis.”
If we examine Scotland’s last published comparative data, we see the unvaccinated enjoyed significant protection from infection compared to the vaccinated:

The above table shows that the age-standardized case rate was growing in the fully vaccinated and boosted compared to the unvaccinated.
In other words, the vaccine effectiveness was negative and growing more negative as time went on.
With regard to severe outcomes like hospitalization, the fully vaccinated had a greater risk than the unvaccinated every week and approached nearly double of the unvaccinated by the end of the reporting period:

PHS highlighted the advantage the boosted had over the unvaccinated in green. Was that the intent? Or was it to distract us from what was happening in the fully vaccinated?
Finally, with regard to COVID-19 mortality, once again the fully vaccinated were at a greater risk of dying:

Boosted Scots remained at lower risk of dying than the unvaccinated as the green shading accentuates.
Nevertheless, the last time Scotland reported these numbers the fully vaccinated were doing worse against the very disease the vaccine was intended to protect them from.
UK stops publishing data because . . . no more free COVID testing?
The UK Health Security Agency’s weekly reports also once included a section called “Vaccination status in cases, deaths and hospitalisations.”
However, in the Week 14 report, released April 7, the agency announced, “Data on the vaccination status of COVID-19 cases, and deaths and hospitalisations with COVID-19, is no longer published.”
In the relevant section of the report, it states:
“From 1 April 2022, the UK Government ended provision of free universal COVID-19 testing for the general public in England, as set out in the plan for living with COVID-19.
“Such changes in testing policies affect the ability to robustly monitor COVID-19 cases by vaccination status, therefore, from the week 14 report onwards this section of the report will no longer be published.
“For further context and previous data, please see previous vaccine surveillance reports and our blog post.”
The agency provided no explanation for why ending free COVID-19 testing would affect reporting of hospitalizations and deaths associated with COVID-19.
The previous week’s report, released on March 31, still had the data in “Table 14. Unadjusted rates of COVID-19 infection, hospitalization and death in vaccinated and unvaccinated populations.”
But unlike the Canadian provinces, the data did not include fully vaccinated individuals, only those who received a booster.
Nonetheless, the data still tell a disappointing story about vaccine effectiveness. Here is the last data reported by the U.K. that compares the unvaccinated to the boosted population:

This table was stratified by age group, and three doses appeared to have little impact on the already very low death rate in people under 50 years old, while deaths in those 80 and older were halved in the boosted group.
What is most remarkable is that in every age group, the risk of contracting COVID-19 was 3 to 5 times higher in boosted individuals than in the unvaccinated. Given the inferior protection provided by full vaccination alone, we can surmise that the fully vaccinated fared even worse.
The United States
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) does report deaths by vaccination status, but does not include boosted individuals.
The data also are nearly three months old, despite assurances that these numbers are updated monthly. There are too few deaths in the under-18 age category to report.
CDC data indicate that as of May 2022, in the 30 to 49 age group, about 1 million people needed to be vaccinated to prevent a single COVID-19 death per week.
That number is nearly 3 million for adults ages 18 to 29.
When will the CDC resume its reporting on COVID-19 deaths, if ever? And, why did the CDC stop comparing hospitalizations in the unvaccinated to those who completed the primary series (unboosted) back in November 2021?
As in the U.K., comparisons are made with the boosted only.
Unlike the Canadian provinces, Scotland and the U.K., the CDC has yet to make a formal announcement about ending reporting of COVID-19 outcomes between the vaccinated and unvaccinated.
Instead, the agency seems to have tacitly admitted that the available vaccines are essentially ineffective by issuing “streamlined” guidelines that do not differentiate by vaccine status as of August 11.
Though the CDC is signaling we can relax restrictions on the unvaccinated, let us not forget that the “latest data” from Manitoba, the U.K. and Scotland indicated COVID-19 outcomes were worse in the fully vaccinated and had been trending downward prior to the mysterious and concurrent decision by multiple public health agencies to end such reporting.
Some of the “latest data” were reported more than six months ago. How are the vaccinated doing now?
Recent Comments